Collision Pointers
Degrees in Graphs
-
Degree
- The degree of a vertex of a graph is the number of edges that are incident to the vertex,
- In multigraph,loops are counted twice
-
Indegree (in DAG)
- Indegree of vertex V is the number of edges which are coming into the vertex V.
-
Outdegree (in DAG)
- Outdegree of vertex V is the number of edges which are going out from the vertex V.
Directed Graph
One thing we have to think carefully is that unlike tree data structure, Graphs can be visited more than once. So we have to be aware of that.
- We want to make sure that we visit all the vertices!
Below code works for when every node is quite strongly connected and assuming there will be no left out ones.
# V: A list of vertices/ adj: adjacency list / s: vertex we are visiting
parent = {s: None}
def dfs_visit(V, adj, s):
for v in adj[s]:
if v not in parent:
parent[v] = s
dfs_visit(V, adj, v)But what if some graphs are not strongly connected and there are more than one cluster? For those cases we can use the above function recursively like below! And this methodology should be used usually for Graph DFS!
def dfs(V, adj):
parent = {}
for s in V:
if s not in parent: # This means we didn't visit s
parent[s] = None
dfs_visit(v, adj, s) # So let's visit s!Time Complexity: O(V + E) —> Linear Time
- The above code will make directed graph get visited once and undirected graph get visited twice(one from each side)
Undirected Graph
Edge Classification
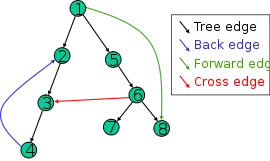
-
Tree edge: the edge that leads us to new edge (it forms a tree in the end that’s why it’s called that way)
-
Forward edge: takes node to descendant in the tree
-
Backward edge: takes node to ancestor in the tree
-
Cross edge: takes sibling node to sibling node in the tree
To detect Forward edge, Cross edge —> use counter for it just like the level!
To detect backward edge: use stack to see if the current node
You can’t have forward edges and cross edges in undirected graphs (Still can have tree edges and Backward edges)